征程 6E/M|如何解決量化部署時 mul 與 bool 類型數(shù)據(jù)交互的問題
一、引言
使用 征程 6 工具鏈進(jìn)行量化部署時,涉及 bool 類型數(shù)據(jù)計算時,會有一些與全 float 計算不同的情況,需要特別注意。
本文將重點結(jié)合 PyTorch 的 torch.mul(逐元素相乘)以及張量的 類型提升(Type Promotion) 規(guī)則,分析在 征程 6 工具鏈上 量化部署時 mul 與 bool 類型數(shù)據(jù)交互的問題。
二、bool 計算示例
在 PyTorch 中,bool 類型的數(shù)據(jù)用于表示 掩碼(mask),常見的操作包括 torch.logical_not()、比較運(yùn)算符(如 ==)等。當(dāng) bool 類型數(shù)據(jù)與其他數(shù)據(jù)類型進(jìn)行算術(shù)運(yùn)算時,PyTorch 會遵循 類型提升(Type Promotion) 規(guī)則,將 bool 轉(zhuǎn)換為更高精度的數(shù)值類型。例如:
import torch x = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0]) y = torch.tensor([True, False, True]) result = x * y # 逐元素相乘 print(result) # tensor([1., 0., 3.]) print(result.dtype) # torch.float32
在這個例子中,bool 類型的 y 在計算時被提升為 float32 類型,因此計算結(jié)果仍然是 float32。
torch.mul 官方文檔里確實沒明確說支持 bool 類型輸入(官網(wǎng)鏈接),但 PyTorch 底層的張量操作支持 bool,是一種 隱式支持,官方文檔默認(rèn)大家了解 PyTorch 的 類型提升(type promotion)規(guī)則。
三、模型中 bool 量化問題分析
在量化模型中,當(dāng) bool 數(shù)據(jù)在計算過程中發(fā)生類型提升,特別是浮點數(shù)過了 quant,再進(jìn)行比較,可能會出現(xiàn)很大的量化誤差。代碼示例如下:
class small_model(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(small_model, self).__init__() self.quant = QuantStub() self.dequant = DeQuantStub() def forward(self, actors_input): actors_input = self.quant(actors_input) print("actors_input:", actors_input) # actors_mask = torch.logical_not(actors_input[:, :, :, -1] == 0) # 一定程度上正確寫法 actors_mask = actors_input[:, :, :, -1] == 1 # 錯誤寫法,會導(dǎo)致 calib 指標(biāo)崩掉 print("actors_mask", actors_mask) print("actors_mask shape:", actors_mask.shape) print("actors_mask[:, :, :, None] shape:", actors_mask[:, :, :, None]。shape) actors_output = actors_input * actors_mask[:, :, :, None] return self.dequant(actors_output) model = small_model() ## ================================================================# # 生成隨機(jī)數(shù)據(jù) # torch.manual_seed(41) # actors_data = torch.randn(1, 2, 4, 3) # actors_mask = torch.randint(0, 2, (1, 2, 4, 1), dtype=torch.bool) # example_input = torch.cat([actors_data, actors_mask], dim=-1) example_input = torch.tensor([[[[ 0.2465, -0.4717, 60.5, 1.0000], [-0.2124, 0.5660, -1.6637, 0.0000], [ 0.3338, 1.6051, -1.5088, 1.0000], [-0.9215, -0.5901, 1.4871, 0.0000]], [[ 0.1650, -0.3785, 1.6710, 0.0000], [-0.3752, 0.2337, 0.4186, 0.0000], [-0.2221, -0.1745, -0.6064, 1.0000], [ 0.9174, -0.6317, 0.6133, 1.0000]]]]) print("example_input:", example_input) ## ================================================================# output = model(example_input) print("float output:", output)
使用 actors_mask = actors_data[:, :, :, -1] == 1 來生成布爾掩碼。
example_input: tensor([[[[ 0.2465, -0.4717, 60.5, 1.0000], [-0.2124, 0.5660, -1.6637, 0.0000], [ 0.3338, 1.6051, -1.5088, 1.0000], [-0.9215, -0.5901, 1.4871, 0.0000]], [[ 0.1650, -0.3785, 1.6710, 0.0000], [-0.3752, 0.2337, 0.4186, 0.0000], [-0.2221, -0.1745, -0.6064, 1.0000], [ 0.9174, -0.6317, 0.6133, 1.0000]]]]) actors_input: tensor([[[[ 0.2465, -0.4717, 60.5, 1.0000], [-0.2124, 0.5660, -1.6637, 0.0000], [ 0.3338, 1.6051, -1.5088, 1.0000], [-0.9215, -0.5901, 1.4871, 0.0000]], [[ 0.1650, -0.3785, 1.6710, 0.0000], [-0.3752, 0.2337, 0.4186, 0.0000], [-0.2221, -0.1745, -0.6064, 1.0000], [ 0.9174, -0.6317, 0.6133, 1.0000]]]]) actors_mask tensor([[[ True, False, True, False], [False, False, True, True]]]) actors_mask shape torch.Size([1, 2, 4]) actors_mask[:, :, :, None] shape torch.Size([1, 2, 4, 1]) float output: tensor([[[[ 0.2465, -0.4717, 60.5, 1.0000], [-0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000], [ 0.3338, 1.6051, -1.5088, 1.0000], [-0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]], [[ 0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000], [-0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000], [-0.2221, -0.1745, -0.6064, 1.0000], [ 0.9174, -0.6317, 0.6133, 1.0000]]]])
打印的結(jié)果如上,可以看到,float 輸出沒有任何問題。
然而,在 量化模型 中,這種 bool mask 運(yùn)算會由于微小的量化誤差發(fā)生非常大的變化,原因在:
actors_data = self.quant(actors_data) actors_mask = actors_data[:, :, :, -1] == 1
數(shù)值 1 經(jīng)過量化反量化后,可能會產(chǎn)生一個或多個 scale 的誤差,原本是 1 的位置就不再是 1 了,會變成 0.9x 或 1.0x,這樣就==1 就不再是 True 了。

打印看到 actors_mask 全部均為 False。
=========set_fake_quantize(calib_model, FakeQuantState.VALIDATION)========= actors_input: QTensor( data = tensor([[[[ 0.2474, -0.4708, 60.4991, 1.0007], [-0.2123, 0.5668, -1.6636, 0.0000], [ 0.3342, 1.6045, -1.5085, 1.0007], [-0.9213, -0.5908, 1.4863, 0.0000]], [[ 0.1643, -0.3785, 1.6709, 0.0000], [-0.3748, 0.2345, 0.4191, 0.0000], [-0.2216, -0.1754, -0.6056, 1.0007], [ 0.9176, -0.6314, 0.6130, 1.0007]]]]), scale = tensor([0.0018]), zero_point = tensor([0]), dtype = qint16, per_channel_axis = -1, is_quantized = False ) actors_mask tensor([[[False, False, False, False], [False, False, False, False]]]) actors_mask shape: torch.Size([1, 2, 4]) actors_mask[:, :, :, None] shape: torch.Size([1, 2, 4, 1]) calib_model out: tensor([[[[0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.]], [[0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.]]]])
這種結(jié)果明顯是不符合預(yù)期的。
四、bool 量化問題解決
怎么修改呢?如下所示
actors_mask = torch.logical_not(actors_data[:, :, :, -1] == 0) # 一定程度上正確寫法 # actors_mask = actors_data[:, :, :, -1] == 1 # 錯誤寫法,會導(dǎo)致calib指標(biāo)崩掉
0 經(jīng)過對稱量化,依舊是 0,再經(jīng)過 logical_not 即可。此時輸出變?yōu)椋航Y(jié)果是正確的。
=========set_fake_quantize(calib_model, FakeQuantState.VALIDATION)========= actors_input: QTensor( data = tensor([[[[ 0.2474, -0.4708, 60.4991, 1.0007], [-0.2123, 0.5668, -1.6636, 0.0000], [ 0.3342, 1.6045, -1.5085, 1.0007], [-0.9213, -0.5908, 1.4863, 0.0000]], [[ 0.1643, -0.3785, 1.6709, 0.0000], [-0.3748, 0.2345, 0.4191, 0.0000], [-0.2216, -0.1754, -0.6056, 1.0007], [ 0.9176, -0.6314, 0.6130, 1.0007]]]]), scale = tensor([0.0018]), zero_point = tensor([0]), dtype = qint16, per_channel_axis = -1, is_quantized = False ) actors_mask tensor([[[ True, False, True, False], [False, False, True, True]]]) actors_mask shape: torch.Size([1, 2, 4]) actors_mask[:, :, :, None] shape: torch.Size([1, 2, 4, 1]) calib_model out: tensor([[[[ 0.2474, -0.4708, 60.4991, 1.0007], [ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000], [ 0.3342, 1.6045, -1.5085, 1.0007], [ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]], [[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000], [ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000], [-0.2216, -0.1754, -0.6056, 1.0007], [ 0.9176, -0.6314, 0.6130, 1.0007]]]])
這種方案一定正確嗎?答案:不一定是正確的,需要考慮極值問題。另外,由于 mul 不支持輸入為 bool 類型,這兒還會出現(xiàn) cpu 算子問題。
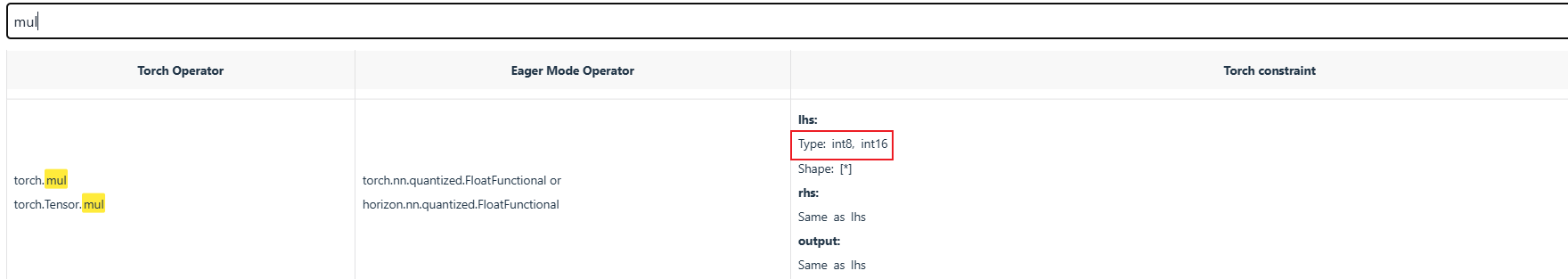
生成的 quantized.onnx 可以看到,確實 mul 運(yùn)行在 cpu 上。
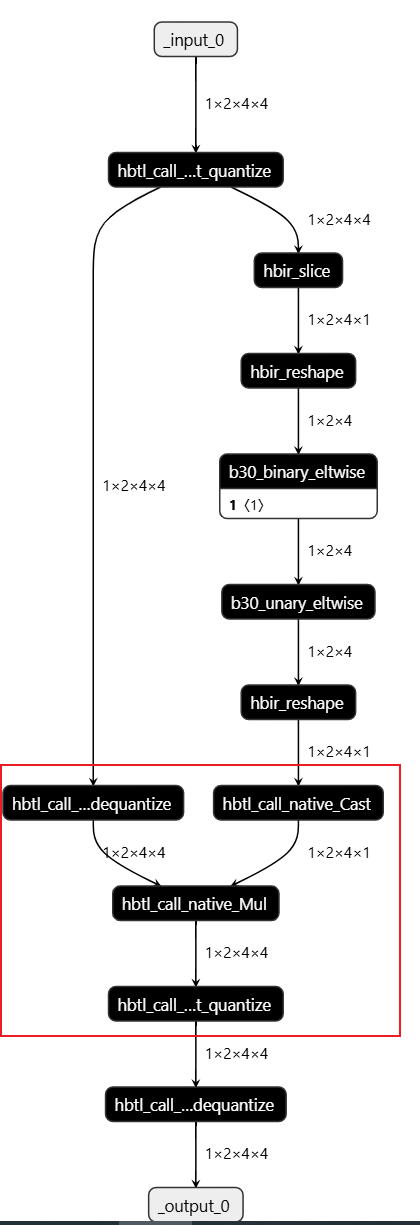
4.1 CPU 算子問題
主要原因是:右側(cè)工具自動進(jìn)行:bool->float32
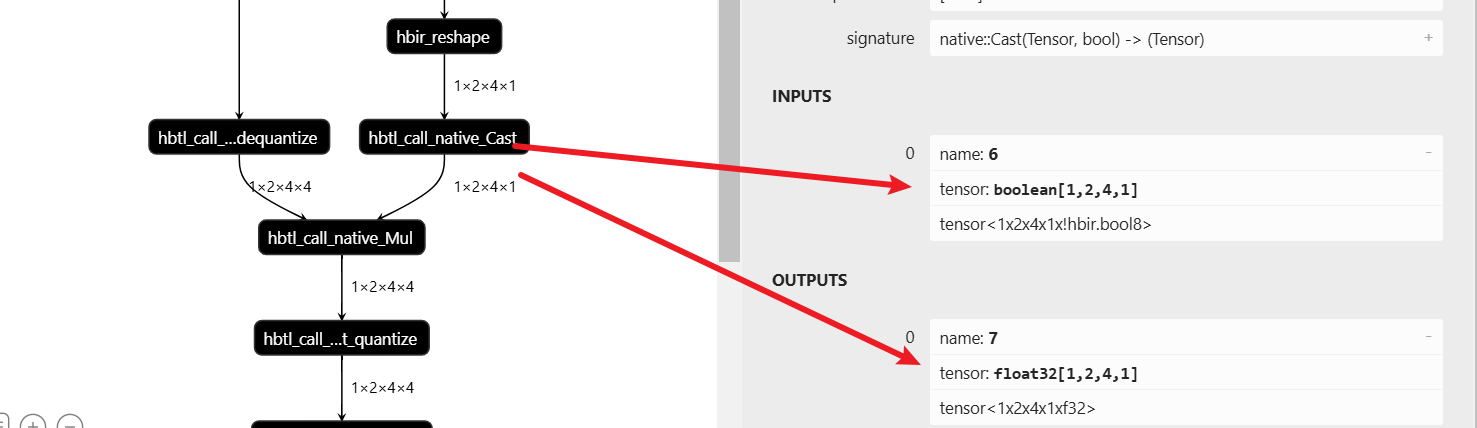
第一個思路是:直接將 actors_mask 轉(zhuǎn) torch.int16,
actors_mask = torch.logical_not(actors_input[:, :, :, -1] == 0).to(torch.int16)
這樣是不行的。因為過了 quant 的 actors_input 是 Qtensor,而。to(torch.int16)強(qiáng)轉(zhuǎn)的 actors_mask 是常規(guī) torch tensor,這也是不行的。
接著就可以想到,應(yīng)該轉(zhuǎn) float,然后過 quant,修改如下:
actors_mask = torch.logical_not(actors_input[:, :, :, -1] == 0).to(torch.float) # 一定程度上正確寫法 actors_mask = self.quant_mask(actors_mask)
此時 mul 左右兩邊都是 qtensor,打印信息如下:
=========set_fake_quantize(calib_model, FakeQuantState.VALIDATION)========= actors_input: QTensor( data = tensor([[[[ 0.2474, -0.4708, 60.4991, 1.0007], [-0.2123, 0.5668, -1.6636, 0.0000], [ 0.3342, 1.6045, -1.5085, 1.0007], [-0.9213, -0.5908, 1.4863, 0.0000]], [[ 0.1643, -0.3785, 1.6709, 0.0000], [-0.3748, 0.2345, 0.4191, 0.0000], [-0.2216, -0.1754, -0.6056, 1.0007], [ 0.9176, -0.6314, 0.6130, 1.0007]]]]), scale = tensor([0.0018]), zero_point = tensor([0]), dtype = qint16, per_channel_axis = -1, is_quantized = False ) actors_mask QTensor( data = tensor([[[1.0000, 0.0000, 1.0000, 0.0000], [0.0000, 0.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000]]]), scale = tensor([3.0518e-05]), zero_point = tensor([0]), dtype = qint16, per_channel_axis = -1, is_quantized = False ) actors_mask shape: (1, 2, 4) actors_mask[:, :, :, None] shape: (1, 2, 4, 1) calib_model out: tensor([[[[ 0.2474, -0.4708, 60.4972, 1.0007], [ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000], [ 0.3342, 1.6045, -1.5085, 1.0007], [ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]], [[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000], [ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000], [-0.2216, -0.1754, -0.6056, 1.0007], [ 0.9176, -0.6314, 0.6130, 1.0007]]]])
可以看到,是全一段 BPU。
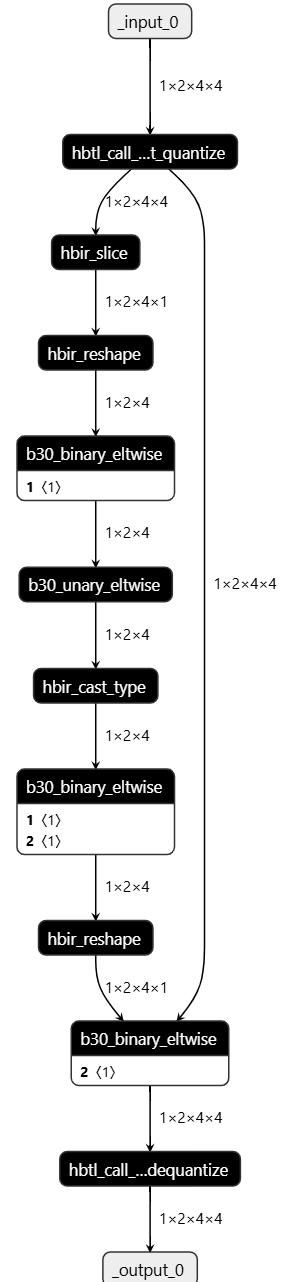
在不考慮極值的影響下,改動完成,此時代碼如下:
class small_model(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(small_model, self).__init__() self.quant = QuantStub() self.dequant = DeQuantStub() self.quant_mask = QuantStub() def forward(self, actors_input): actors_input = self.quant(actors_input) actors_mask = torch.logical_not(actors_input[:, :, :, -1] == 0).to(torch.float) # 一定程度上正確寫法 actors_mask = self.quant_mask(actors_mask) actors_output = actors_input * actors_mask[:, :, :, None] # + - * / return self.dequant(actors_output) model = small_model() ## ================================================================# # 生成隨機(jī)數(shù)據(jù) # torch.manual_seed(41) # actors_data = torch.randn(1, 2, 4, 3) # actors_mask = torch.randint(0, 2, (1, 2, 4, 1), dtype=torch.bool) # example_input = torch.cat([actors_data, actors_mask], dim=-1) example_input = torch.tensor([[[[ 0.2465, -0.4717, 60.5, 1.0000], [-0.2124, 0.5660, -1.6637, 0.0000], [ 0.3338, 1.6051, -1.5088, 1.0000], [-0.9215, -0.5901, 1.4871, 0.0000]], [[ 0.1650, -0.3785, 1.6710, 0.0000], [-0.3752, 0.2337, 0.4186, 0.0000], [-0.2221, -0.1745, -0.6064, 1.0000], [ 0.9174, -0.6317, 0.6133, 1.0000]]]]) print("example_input:", example_input) ## ================================================================# output = model(example_input) print("float output:", output)
4.2 極值問題bool 被其他極大值 影響
如果模型輸入 actors_input 有極大值存在,例如 70000,int16 量化,會將 actors_mask 原本是 1 的地方給變?yōu)?0,量化輸出示例如下:
=========set_fake_quantize(calib_model, FakeQuantState.VALIDATION)========= actors_input: QTensor( data = tensor([[[[ 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 6.9999e+04, 0.0000e+00], [ 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, -2.1363e+00, 0.0000e+00], [ 0.0000e+00, 2.1363e+00, -2.1363e+00, 0.0000e+00], [ 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 2.1363e+00, 0.0000e+00]], [[ 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 2.1363e+00, 0.0000e+00], [ 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00], [ 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00], [ 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00]]]]), scale = tensor([2.1363]), zero_point = tensor([0]), dtype = qint16, per_channel_axis = -1, is_quantized = False ) actors_mask QTensor( data = tensor([[[0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.]]]), scale = tensor([3.0518e-05]), zero_point = tensor([0]), dtype = qint16, per_channel_axis = -1, is_quantized = False ) calib_model out: tensor([[[[0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.]], [[0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.]]]])
根據(jù)量化公式:
quantized=clamp(round(float/scale),qmin,qmax)
float:浮點數(shù) 數(shù)據(jù),即 fp32(32-bit 浮點數(shù))表示的張量值。
scale:縮放因子(scale factor),用于將浮點數(shù)縮放到整數(shù)范圍(量化尺度)。
round(float/scale):對縮放后的值進(jìn)行四舍五入,得到量化的整數(shù)表示。
clamp(…, qmin, qmax):將量化值限制在 最小值 qmin 和 最大值 qmax 之間,防止溢出。
在這個示例中,scale = 70000/32767 = 2.1263。bool 類型的 1,經(jīng)過量化:round(1 / 2.1263)=0,由于 round 舍入誤差的存在,原來的 1 也被變?yōu)榱?0,再經(jīng)過反量化也拯救不了這個舍入誤差了。
bool 1 作為 極大值 的影響
如果模型輸入 actors_data 都是非常小的數(shù)值,由于 bool 類型 1 的存在,會導(dǎo)致 1 成為極大值,影響量化 scale 的統(tǒng)計,繼而影響其他數(shù)值的量化精細(xì)程度。
所以,最穩(wěn)妥的方式,是將 actor_data 與 actor_mask 分開送入模型。actor_data 自己過 quant,actor_mask 自己過 quant_mask。
4.3 解決方案示例bool 類型已經(jīng)變 為 0/1 的 float,可以這么寫。需要注意,一定是只有 0 / 1 的 float,在模型中間也可以這么寫。
class small_model(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(small_model, self).__init__() self.quant = QuantStub() self.quant_mask = QuantStub() self.dequant = DeQuantStub() def forward(self, actors_input): actors_mask = actors_input[:, :, :, -1] actors_mask = self.quant_mask(actors_mask) # 這種寫法會導(dǎo)致模型輸入位置有兩個量化節(jié)點,且 scale 不同而刪不掉, 未來用 vpu 可以這么寫 actors_data = actors_input[:,:,:,:-1] actors_data = self.quant(actors_data) # 這種寫法會導(dǎo)致模型輸入位置有兩個量化節(jié)點,且 scale 不同而刪不掉, 未來用 vpu 可以這么寫 print("actors_data:", actors_data) print("actors_mask", actors_mask) actors_output = actors_data * actors_mask[:, :, :, None] # + - * / return self.dequant(actors_output) model = small_model() ## ================================================================# # 生成隨機(jī)數(shù)據(jù) # torch.manual_seed(41) # actors_data = torch.randn(1, 2, 4, 3) # actors_mask = torch.randint(0, 2, (1, 2, 4, 1), dtype=torch.bool) # example_input = torch.cat([actors_data, actors_mask], dim=-1) example_input = torch.tensor([[[[ 0.2465, -0.4717, 70000, 1.0000], [-0.2124, 0.5660, -1.6637, 0.0000], [ 0.3338, 1.6051, -1.5088, 1.0000], [-0.9215, -0.5901, 1.4871, 0.0000]], [[ 0.1650, -0.3785, 1.6710, 0.0000], [-0.3752, 0.2337, 0.4186, 0.0000], [-0.2221, -0.1745, -0.6064, 1.0000], [ 0.9174, -0.6317, 0.6133, 1.0000]]]]) print("example_input:", example_input) output = model(example_input) print("float output:", output)
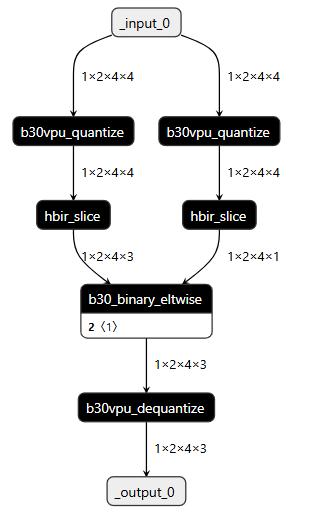
如果是模型首部,且確實是 bool 輸入
class small_model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(small_model, self).__init__()
self.quant = QuantStub()
self.quant_mask = QuantStub()
self.dequant = DeQuantStub()
def forward(self, actors_input):
actors_mask = actors_input["actors_mask"]
actors_data = self.quant(actors_input["actors_data"])
print("actors_data:", actors_data)
print("actors_mask", actors_mask)
actors_output = actors_data * self.quant_mask(actors_mask.to(torch.float)) # + - * /
return self.dequant(actors_output)
# 生成隨機(jī)數(shù)據(jù)
torch.manual_seed(41)
actors_data = torch.randn(1, 2, 4, 3)
actors_mask = torch.randint(0, 2, (1, 2, 4, 1), dtype=torch.bool)
example_input = {"actors_data":actors_data, "actors_mask":actors_mask}
print("example_input:", example_input)
output = model(example_input)
print("float output:", output)
*博客內(nèi)容為網(wǎng)友個人發(fā)布,僅代表博主個人觀點,如有侵權(quán)請聯(lián)系工作人員刪除。